Machine Screw: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. A machine screw is typically designed to be fastened to an existing, tapped hole on a metal surface. | |||
The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. | |||
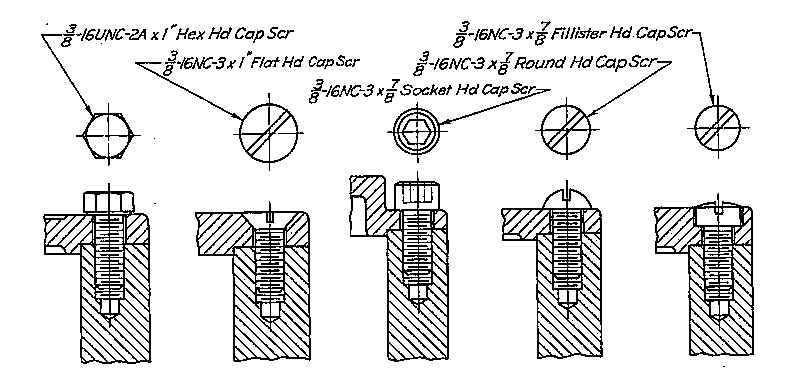
Example: Standard Cap Screws | Example: Standard Cap Screws | ||
| Line 9: | Line 6: | ||
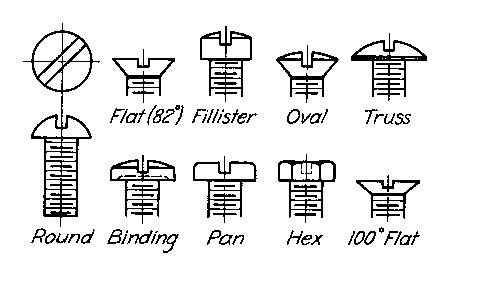
Example: Standard Machine Screw Head Types | Example: Standard Machine Screw Head Types | ||
Screw bit types: | |||
* Slotted | |||
* Phillips | |||
* Combination | |||
* Torx | |||
* Star | |||
* Hex (internal) | |||
* Hex (external) | |||
* JIS | |||
* Phillips Square | |||
* Square | |||
[[File:machine-screw02.png]] | [[File:machine-screw02.png]] | ||
the standard [[Computer Case Screw]] size is 6-32. | the standard [[Computer Case Screw]] size is 6-32. | ||
== Unified Thread Standard (UTS) == | |||
The following formula is used to calculate the major diameter of a numbered screw greater than or equal to 0: Major diameter = Screw # × 0.013" + 0.060". For example, a number 10 calculates as: #10 × 0.013" + 0.060" = 0.190" major diameter. | |||
Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi) | |||
ASME, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, has a document called ASME B1.1 that provides requirements for unified inch screw threads. | |||
{{:Template:Sparse Entry}} | |||
| | ||
Latest revision as of 06:42, 12 June 2019
The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. A machine screw is typically designed to be fastened to an existing, tapped hole on a metal surface.
Example: Standard Cap Screws
Example: Standard Machine Screw Head Types
Screw bit types:
- Slotted
- Phillips
- Combination
- Torx
- Star
- Hex (internal)
- Hex (external)
- JIS
- Phillips Square
- Square
the standard Computer Case Screw size is 6-32.
Unified Thread Standard (UTS)
The following formula is used to calculate the major diameter of a numbered screw greater than or equal to 0: Major diameter = Screw # × 0.013" + 0.060". For example, a number 10 calculates as: #10 × 0.013" + 0.060" = 0.190" major diameter.
Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi)
ASME, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, has a document called ASME B1.1 that provides requirements for unified inch screw threads.
 Learn more... |