Mint Linux Bootable Installation Media: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m →Burn |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
=== Burn === | === Burn === | ||
The | While in the past we used bootable CD ROM discs, then maybe DVD as the ISO files began to bloat, the preferred method is currently the use of bootable solid state media. | ||
There are a number of [[Bootable USB flash drive utilities]] you can use. | |||
For this example we will simply use The dd Command in Linux. | |||
When you insert the USB flash drive into the Linux PC it is immediately recognized as a block device. It will be auto mounted if there is a partition that has a compatible file system. If it is auto mounted you need to unmount it from the command line while not "ejecting" it. We want the kernel to see the block device, however, we do not want any partition mounted. | |||
# insert the USB stick | |||
# unmount the USB stick media if mounted | |||
[[Category:Computer_Technology]] | [[Category:Computer_Technology]] | ||
[[Category:Linux]] | [[Category:Linux]] | ||
Revision as of 08:45, 11 February 2022
You can find out how to download Linux Mint:
Download
It is recommended to use the bittorrent download option for best speed and efficiency.
Verify
Once downloaded, verify your new ISO image file using checksum.
Anyone can produce fake ISO images, it is your responsibility to check you are downloading the official ones.
Download the ISO image then click on the sha256sum.txt and sha256sum.txt.gpg buttons from the Mint web site to see the key hash you can compare to.
Or you can save the SHA256 sums provided by Linux Mint locally.
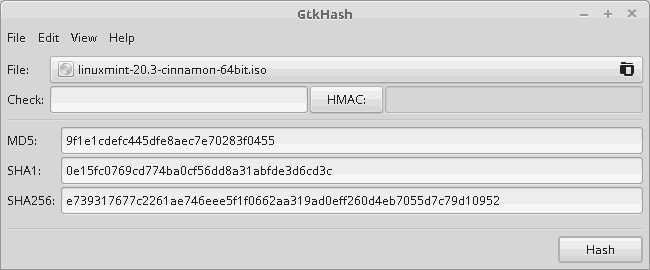
Here is how I did it. After downloading the iso, and for this example we will consider linuxmint-20.3-cinnamon-64bit.iso, I used the program GtkHash.
Then from the web site I compared to the correct hash from
e739317677c2261ae746eee5f1f0662aa319ad0eff260d4eb7055d7c79d10952 *linuxmint-20.3-cinnamon-64bit.iso
Burn
While in the past we used bootable CD ROM discs, then maybe DVD as the ISO files began to bloat, the preferred method is currently the use of bootable solid state media.
There are a number of Bootable USB flash drive utilities you can use.
For this example we will simply use The dd Command in Linux.
When you insert the USB flash drive into the Linux PC it is immediately recognized as a block device. It will be auto mounted if there is a partition that has a compatible file system. If it is auto mounted you need to unmount it from the command line while not "ejecting" it. We want the kernel to see the block device, however, we do not want any partition mounted.
- insert the USB stick
- unmount the USB stick media if mounted