Forced Air Gas Furnace: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
New page: A gas forced-air heating system has a pilot light that ignites a burner inside the combustion chamber, creating heat that is then transferred to the furnace’s heat exchanger, a metal cha... |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
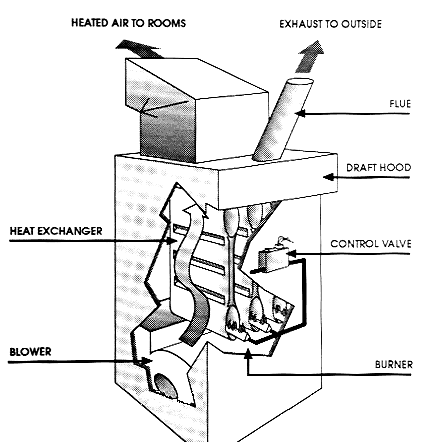
A gas forced-air heating system has a pilot light that ignites a burner inside the combustion chamber, creating heat that is then transferred to the furnace’s heat exchanger, a metal chamber around which air flows and is then heated. That heated air is then forced into the hot-air plenum and into the rooms through ducts. Gas fumes and carbon monoxide are vented through a flue in the roof. The forced air gas furnace provides the option for an attached air conditioning unit and humidifier. | A gas forced-air heating system has a pilot light that ignites a burner inside the combustion chamber, creating heat that is then transferred to the furnace’s heat exchanger, a metal chamber around which air flows and is then heated. That heated air is then forced into the hot-air plenum and into the rooms through ducts. Gas fumes and carbon monoxide are vented through a flue in the roof. The forced air gas furnace provides the option for an attached air conditioning unit and humidifier. | ||
== Gas Furnace Diagram == | |||
[[Image:Typical-forced-air-gfur.gif]] | |||
Revision as of 09:49, 27 September 2010
A gas forced-air heating system has a pilot light that ignites a burner inside the combustion chamber, creating heat that is then transferred to the furnace’s heat exchanger, a metal chamber around which air flows and is then heated. That heated air is then forced into the hot-air plenum and into the rooms through ducts. Gas fumes and carbon monoxide are vented through a flue in the roof. The forced air gas furnace provides the option for an attached air conditioning unit and humidifier.
Gas Furnace Diagram