SATA Hard Drive: Difference between revisions
Created page with "The SATA Hard Disk Drive has been the most popular choice for desktop and laptop computers since around 2002. The Standard Serial ATA Drive is generally available in internal..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[File:sata-drive-connector.gif]] | [[File:sata-drive-connector.gif]] | ||
SATA drives do not use jumpers to designate SLAVE and MASTER relationship for the PC BIOS. The drives are connected with automatic termination in the serial interface. If a jumper is present, it is likely for backwards compatibility. | SATA drives do not use jumpers to designate SLAVE and MASTER relationship for the PC BIOS. The drives are connected with automatic termination in the serial interface because each drive has its own cable. If a jumper is present, it is likely for backwards compatibility. As stated, each SATA disk drive has its own cable that connects directly to a Serial ATA host adapter or a Serial ATA port on your motherboard. Some motherboards have SATA connectors along with legacy connectors. You can use a Serial ATA drive in the same system with Parallel ATA drives as long as both interfaces are supported on the motherboard or with a host adapter. | ||
When the computer is turned on, check the BIOS to see if the drive is detected. If all of your drive controllers are enabled and the drive is properly connected it should be listed. | |||
[[Category:Computer_Technology]] | |||
[[Category:Hardware]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:24, 21 December 2014
The SATA Hard Disk Drive has been the most popular choice for desktop and laptop computers since around 2002. The Standard Serial ATA Drive is generally available in internal configurations for the 3.5" and 2.5" standard. The 3.5" drive is typically used in the desktop computer while the smaller 2.5" drive is generally used in the laptop or notebook computer.
The SATA (Serial ATA) controller type is one of several Drive Controller Types for the PC.
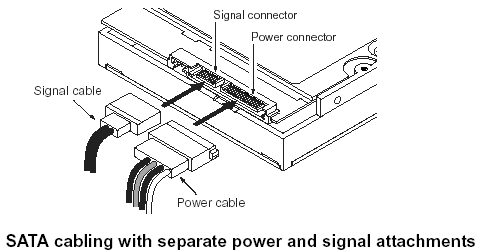
SATA Drive Connection
SATA uses simple cables that are molded to fit on the drive and motherboard connector one way. Most SATA connectors have an L shaped right angle connector.
SATA drives do not use jumpers to designate SLAVE and MASTER relationship for the PC BIOS. The drives are connected with automatic termination in the serial interface because each drive has its own cable. If a jumper is present, it is likely for backwards compatibility. As stated, each SATA disk drive has its own cable that connects directly to a Serial ATA host adapter or a Serial ATA port on your motherboard. Some motherboards have SATA connectors along with legacy connectors. You can use a Serial ATA drive in the same system with Parallel ATA drives as long as both interfaces are supported on the motherboard or with a host adapter.
When the computer is turned on, check the BIOS to see if the drive is detected. If all of your drive controllers are enabled and the drive is properly connected it should be listed.