Difference between revisions of "Windows 10 Tips & Tricks"
(→Command Prompt, System Restore, and other Startup Settings at Boot w/o Boot Disk) |
(→Available Command Prompt at Windows Login Screen) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
\windows\system32\utilman.exe | \windows\system32\utilman.exe | ||
Then we will make a copy of the command shell "cmd.exe" and call it utilman.exe placing it in the same path. | Then we will make a copy of the command shell "cmd.exe" and call it utilman.exe placing it in the same path. | ||
| − | cd \windows\system32 | + | d: |
| − | move | + | cd d:\windows\system32 |
| + | move Utilman.exe Utilman.bak | ||
copy cmd.exe utilman.exe | copy cmd.exe utilman.exe | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 9 June 2016
Contents
Command Prompt, System Restore, and other Startup Settings at Boot w/o Boot Disk
You don't need a boot disk to get to the "Advanced Options" menu.
NOTE: You will boot to a command shell using the recovery environment and not the regular windows environment. Changes made here may not be saved to your normal windows drive! Also you will NOT be able to access the SAM file registry hive, something that does require booting from a boot disk.
From the Windows login screen: hold down shift key while clicking on the power icon in lower right corner. Keep holding down shift key and click on restart.
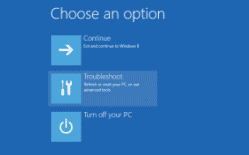
Windows will not restart, but instead show a blue screen with "Choose an option"
- Options are: Continue, Troubleshoot, Turn off your PC.
- Choose: Troubleshoot, then choose Advanced Options
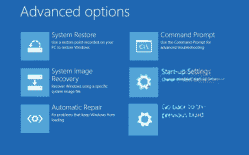
Now you will see a blue screen with six different options.
- Options are: System Restore, System Image Recovery, Startup Repair, Command Prompt, Startup Settings, and Go back to the previous build.
If you select an option, such as "Command Prompt" the computer will reboot and load into a basic graphical interface with a command shell window open and no other windows menus.
Note: Some of the Advanced Options on the screens mentioned above may be different. They should be similar and there should always been an option for the Command Prompt.
Your experience with drive letters may vary from this example. When I get to a command shell I am at a prompt on the X drive. This is the restore partition and not the live windows partition. Typing "d:" and pressing enter will move you to the live windows partition. I have found that C: is not the live partition but another restore/system partition.
Change password from command prompt
In this example we will change the administrator password from the command prompt. An elevated command prompt is required.
Show all users:
net user
Change administrator password:
net user administrator *
The * will cause it to prompt you to enter the password of choice two times.
Other related: To activate the inactive administrator account, run the command
net user administrator /active:yes
If you want to enable the guest account as well run the command
net user guest /active:yes
No Login Password Required
Also known as "Automatic Account Login." We will use the "netplwiz" command to accomplish this.
- Press the Windows + R keys to open the Run dialog box, type "netplwiz"
- Select the User Name of the Microsoft account or local account that you want to have Windows automatically sign in to at startup.
- Uncheck the Users must enter a user name and password to use this computer box
- Enter the password of the selected local account or Microsoft account twice and click OK. If a selected local account does not have a password created for it, then leave the password fields empty. A Microsoft Live account will always have a password.
Available Command Prompt at Windows Login Screen
This is a hack that makes it so the "Ease of Access" icon in the bottom right of the login screen opens a command shell rather than the accessibility menu. This makes it so a command prompt can be available even before a user authenticates into windows.
To accomplish this we will rename or delete the file "utilman.exe" which is located:
\windows\system32\utilman.exe
Then we will make a copy of the command shell "cmd.exe" and call it utilman.exe placing it in the same path.
d: cd d:\windows\system32 move Utilman.exe Utilman.bak copy cmd.exe utilman.exe