Difference between revisions of "Forced Air Gas Furnace"
m |
m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:Typical-forced-air-gfur.gif]] | [[Image:Typical-forced-air-gfur.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This type of furnace produces heat through the combustion of natural gas in the furnace's burner. The heat produced from this process then passes through a heat exchanger. Air from your home's return air ducts is blown over the heat exchanger, thus warming the air. | ||
| + | The furnace's blower then blows the warmed air into the ductwork, which carries and disperses the warmed air throughout the home. | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 27 September 2010
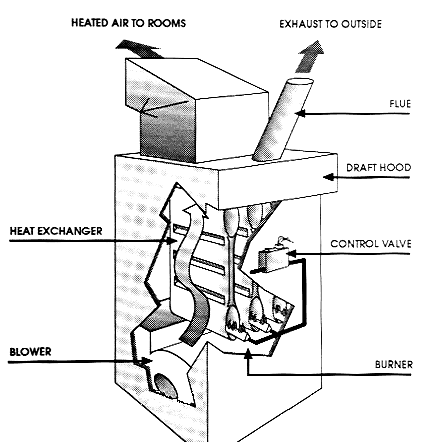
A gas forced-air heating system has a pilot light that ignites a burner inside the combustion chamber, creating heat that is then transferred to the furnace’s heat exchanger, a metal chamber around which air flows and is then heated. That heated air is then forced into the hot-air plenum and into the rooms through ducts. Gas fumes and carbon monoxide are vented through a flue in the roof. The forced air gas furnace provides the option for an attached air conditioning unit and humidifier.
Gas Furnace Diagram
This type of furnace produces heat through the combustion of natural gas in the furnace's burner. The heat produced from this process then passes through a heat exchanger. Air from your home's return air ducts is blown over the heat exchanger, thus warming the air. The furnace's blower then blows the warmed air into the ductwork, which carries and disperses the warmed air throughout the home.