Grade Markings for Steel Fasteners: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Bolt Grade Markings and Tensile Strength - SAE and ASTM. | Bolt Grade Markings and Tensile Strength - SAE and ASTM. | ||
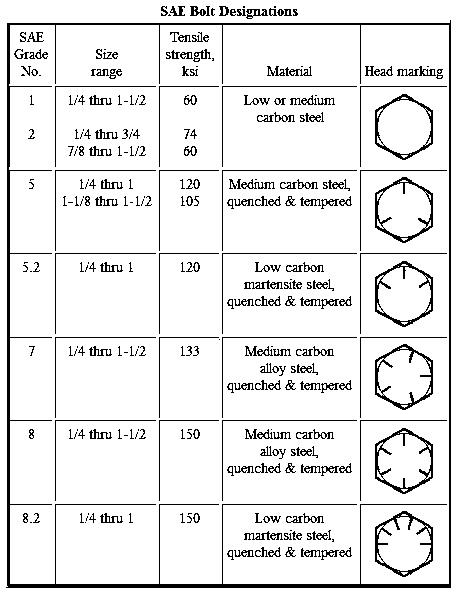
* Bolts,Screws,Studs with no tick marks on the head = Grade 2 | * Bolts,Screws,Studs with no tick marks on the head = Grade 2 ''(same as metric grade 5.8)'' | ||
* Bolts,Screws,Studs with 3 symmetrical tick marks spaced 120° on the head = Grade 5 | * Bolts,Screws,Studs with 3 symmetrical tick marks spaced 120° on the head = Grade 5 ''(same as metric grade 8.8)'' | ||
* Bolts,Screws,Studs with 5 symmetrical tick marks spaced 72° on the head = Grade 7 | * Bolts,Screws,Studs with 5 symmetrical tick marks spaced 72° on the head = Grade 7 | ||
* Bolts,Screws,Studs with 6 symmetrical tick marks spaced 60° on the head = Grade 8 | * Bolts,Screws,Studs with 6 symmetrical tick marks spaced 60° on the head = Grade 8 ''(same as metric grade 10.9)'' | ||
Grade 8 fasteners are the strongest with a minimum tensile strength of 150ksi for all diameters from ¼ inch through 1-1/2 inches. They are required to be heat-treated, quenched, and tempered. | |||
[[File:WikiSAEFastenerDesignations.png]] | |||
The '''Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE)''' has a standard called SAE J429 Mechanical And Material Requirements for Mechanical Fasteners. The standard introduces a designation system based on numbers where increasing numbers indicate increasing tensile strength. Another organization, ASTM International, formerly known as '''American Society for Testing and Materials''', is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards. ASTM fastener standards specify and test the properties of mechanical fasteners such as bolts, nuts, screws, and other hardware fasteners. The SAE steel grades system is a standard alloy numbering systems for steel grades maintained by SAE International. In the 1930s and 1940s the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and SAE were both involved in efforts to standardize such a numbering system for steels. In 1995 the AISI turned over future maintenance of the system to SAE for reasons including elimination of redundancy. | |||
*Note that the SAE steel grade system's correspondence to other alloy numbering systems, such as the ASTM-SAE unified numbering system (UNS) | |||
*Inch-series fasteners utilize standards ASTM A307, ASTM A354, and ASTM A193 | |||
ASTM A490 and ASTM A490M are ASTM International standards for heavy hex structural bolts made from alloy steel. ASTM A490 bolts are equivalent to ASTM A325 bolts in application and geometry, but are made to a higher strength. The imperial grades are made to the same strength specifications as ASTM A354 grade BD. The metric grades are made to the same strength specifications as ASTM F568M property class 10.9. The head markings may be alphanumeric or non-symmetrical tick marks. | |||
[[Category:Construction]] | [[Category:Construction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:03, 12 June 2019
Bolts (non-metric) and all fasteners are made to meet certain strength requirements and have a grade or ASTM rating. Special markings on screw heads and nuts identify the fastener's grade. Bolts and screws have a grade and manufacturer identification marking. Screws and bolts above 1/4" are typically marked on the top of their head unless Grade 2.
Bolt Grade Markings and Tensile Strength - SAE and ASTM.
- Bolts,Screws,Studs with no tick marks on the head = Grade 2 (same as metric grade 5.8)
- Bolts,Screws,Studs with 3 symmetrical tick marks spaced 120° on the head = Grade 5 (same as metric grade 8.8)
- Bolts,Screws,Studs with 5 symmetrical tick marks spaced 72° on the head = Grade 7
- Bolts,Screws,Studs with 6 symmetrical tick marks spaced 60° on the head = Grade 8 (same as metric grade 10.9)
Grade 8 fasteners are the strongest with a minimum tensile strength of 150ksi for all diameters from ¼ inch through 1-1/2 inches. They are required to be heat-treated, quenched, and tempered.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has a standard called SAE J429 Mechanical And Material Requirements for Mechanical Fasteners. The standard introduces a designation system based on numbers where increasing numbers indicate increasing tensile strength. Another organization, ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards. ASTM fastener standards specify and test the properties of mechanical fasteners such as bolts, nuts, screws, and other hardware fasteners. The SAE steel grades system is a standard alloy numbering systems for steel grades maintained by SAE International. In the 1930s and 1940s the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and SAE were both involved in efforts to standardize such a numbering system for steels. In 1995 the AISI turned over future maintenance of the system to SAE for reasons including elimination of redundancy.
- Note that the SAE steel grade system's correspondence to other alloy numbering systems, such as the ASTM-SAE unified numbering system (UNS)
- Inch-series fasteners utilize standards ASTM A307, ASTM A354, and ASTM A193
ASTM A490 and ASTM A490M are ASTM International standards for heavy hex structural bolts made from alloy steel. ASTM A490 bolts are equivalent to ASTM A325 bolts in application and geometry, but are made to a higher strength. The imperial grades are made to the same strength specifications as ASTM A354 grade BD. The metric grades are made to the same strength specifications as ASTM F568M property class 10.9. The head markings may be alphanumeric or non-symmetrical tick marks.