Difference between revisions of "Analog TV and Digital Video Resolution Guide"
(New page: In analog video the image consists of television lines, and in digital the picture is made up of picture elements otherwise known as pixels. In North America and Japan, the NTSC standard...) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In analog video the image consists of television lines, and in digital the picture is made up of picture elements otherwise known as pixels. In North America and Japan, the NTSC standard (National Television System Committee) is the predominant analog video standard, while in Europe the PAL standard (Phase Alternation by Line) is used. NTSC has a resolution of 480 lines, and uses a refresh rate of 60 interlaced fields per second (or 30 full frames per second). | In analog video the image consists of television lines, and in digital the picture is made up of picture elements otherwise known as pixels. In North America and Japan, the NTSC standard (National Television System Committee) is the predominant analog video standard, while in Europe the PAL standard (Phase Alternation by Line) is used. NTSC has a resolution of 480 lines, and uses a refresh rate of 60 interlaced fields per second (or 30 full frames per second). | ||
| + | |||
| + | == TV == | ||
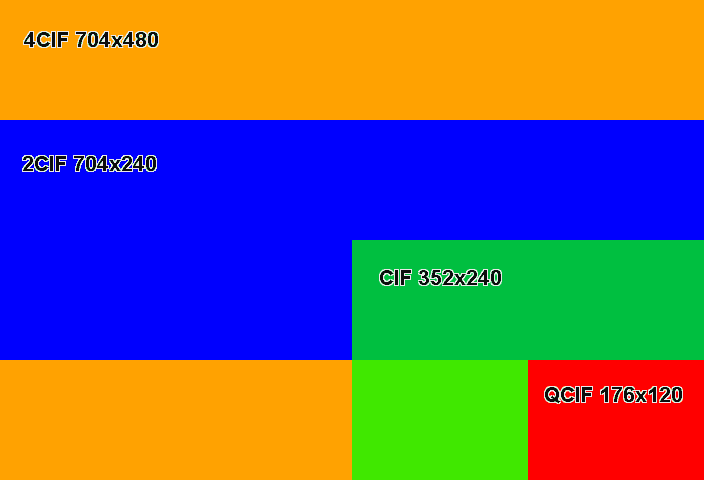
When analog video is digitized, the maximum amount of pixels that can be created is based on the number of TV lines available to be digitized. In NTSC the maximum size of the digitized image is 720x480 pixels. | When analog video is digitized, the maximum amount of pixels that can be created is based on the number of TV lines available to be digitized. In NTSC the maximum size of the digitized image is 720x480 pixels. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
* 720x480 pixels max for NTSC | * 720x480 pixels max for NTSC | ||
* 2CIF resolution = 704x240 (NTSC) | * 2CIF resolution = 704x240 (NTSC) | ||
| + | * CIF 352x240 (NTSC) | ||
2CIF works by dividing the number of horizontal lines by 2. To compensate for motion blur, each horizontal line is shown twice, a practice known as line doubling. | 2CIF works by dividing the number of horizontal lines by 2. To compensate for motion blur, each horizontal line is shown twice, a practice known as line doubling. | ||
[[Image:analogvidreschartcif.png]] | [[Image:analogvidreschartcif.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == VGA == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Digital VGA resolution is defined by pixels, and the VGA standard is 640x480 pixels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * VGA 640x480 pixels | ||
| + | * Quarter VGA (QVGA, SIF) 320x240 pixels, ''compare to CIF'' | ||
| + | * XVGA 1024x768 pixels | ||
| + | * 4xVGA 280x960 pixels | ||
| + | |||
| + | QVGA is sometimes called SIF (Standard Interchange Format) resolution, which can be easily confused with CIF. | ||
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MPEG == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 11 April 2008
In analog video the image consists of television lines, and in digital the picture is made up of picture elements otherwise known as pixels. In North America and Japan, the NTSC standard (National Television System Committee) is the predominant analog video standard, while in Europe the PAL standard (Phase Alternation by Line) is used. NTSC has a resolution of 480 lines, and uses a refresh rate of 60 interlaced fields per second (or 30 full frames per second).
TV
When analog video is digitized, the maximum amount of pixels that can be created is based on the number of TV lines available to be digitized. In NTSC the maximum size of the digitized image is 720x480 pixels.
- 720x480 pixels max for NTSC
- 2CIF resolution = 704x240 (NTSC)
- CIF 352x240 (NTSC)
2CIF works by dividing the number of horizontal lines by 2. To compensate for motion blur, each horizontal line is shown twice, a practice known as line doubling.
VGA
Digital VGA resolution is defined by pixels, and the VGA standard is 640x480 pixels.
- VGA 640x480 pixels
- Quarter VGA (QVGA, SIF) 320x240 pixels, compare to CIF
- XVGA 1024x768 pixels
- 4xVGA 280x960 pixels
QVGA is sometimes called SIF (Standard Interchange Format) resolution, which can be easily confused with CIF.
MPEG