Radio Frequencies, Bands, and Channels: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
| style="text-align:center;"| 9 | | style="text-align:center;"| 9 | ||
| style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3000 MHz<br />1 m – 100 mm | | style="text-align:center; white-space:nowrap;"| 300–3000 MHz<br />1 m – 100 mm | ||
| style="text-align:center;" | Television broadcasts, microwave oven, microwave devices/communications, [[radio astronomy]], [[mobile phone]]s, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee, GPS and two-way radios such as land mobile, [[Family Radio Service|FRS]] and [[GMRS]] radios, amateur radio | | style="text-align:center;" | Television broadcasts, microwave oven, microwave devices/communications, [[radio astronomy]], [[mobile phone]]s, wireless LAN, [[Bluetooth]], ZigBee, GPS and two-way radios such as land mobile, [[Family Radio Service|FRS]] and [[GMRS]] radios, amateur radio | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Super high frequency]] | | [[Super high frequency]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:58, 23 August 2017
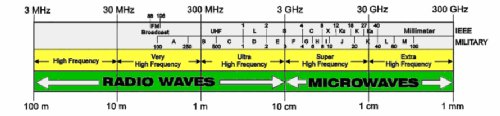
Radio frequency transmissions are divided up into contiguous bands for different purposes. These groupings are usually due to the different physical characteristics or behavior of radio waves at different frequencies. To understand the properties of different radio waves, first calculate the wavelength of some typical radio frequencies found in each of the main broadcast bands. This is performed by dividing the speed of light by the frequency of interest. However, electricity travels at 95% the speed of light in a wire, the number of times the polarity changes in one second (frequency) determines how long the wire has to be in order to be resonant.
Radio is divided into bands. The Long Wave Band (LW) starts at 30 kHz and goes to 300 kHz. The Medium Wave Band (MW) is from 300 kHz to 3000 kHz or 3 MHz. The High Frequency Band (HF) is from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The Very High Frequency Band (VHF) is from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. The Ultra-High Frequency Band (UHF) is from 300 MHz to 3000 MHz or 3 GHz. Above these frequencies are several microwave bands which are defined as the Super High Frequency Band (SHF).
- Band: MF — Medium Frequency — AM (amplitude mall/ago/0 Radio Band (535-1705 kHz)
- Channel: AM Radio — 1120 kHz 300 million meters/sec ÷ 1120 thousand cycles /sec = 268 meters (880 feet)
- Band: VHF — Very High Frequency FM Viequeney moduilatiaii) Radio Band (88-108 MHz)
- Channel: FM Radio — 98.1 MHz 300 million meters/sec = 98.1 million cycles/sec = 3 meters (10 feet)
- Band: VHF — Very High Frequency — Television Band (54-216 MHz)
- Channel: VHF TV, Channel 8-183 MHz 300 million meters/sec ÷ 183 million cycles/sec = 1.64 meters (5 feet)
- Band: UHF — Ultra High Frequency — Television Band (470-806 MHz)
- Channel: UHF TV, Channel 40 — 629 MHz 300 million meters/sec ÷ 629 million cycles/sec = 0.48 meters (19 inches)
- Band: SHF — Super High Frequency — Broadcasting Satellite Ku Band (11-14 GHz)
- Channel: Direct Broadcast Satellite, Transponder 30 — 12.647 GHz 300 million meters/sec ÷ 12.647 billion cyclesfsec = 2.37 centimeters (1 inch)
As this summary of the Electromagnetic Spectrum illustrates, the wavelengths of different broadcast bands vary quite a bit, from hundreds of feet to an inch or less. Because of these differing wavelengths, there are major physical differences in the design of antenna types used to transmit and receive signals in different bands. The amplitudes (or power) of these signals also greatly influence the design and size of these antennas.
Each radio band is divided into individual channels, and each of these channels includes a range of frequencies. The range of frequencies included in a channel from lowest to highest is known as the channel's batidwidin. (The term may also refer to any particular range of frequencies, not just those in RF.) For simplicity, however, a channel is often identified by its reizterfrequency, so that only one numerical value (rather than two) will have to be cited when referring to a particular channel. If the center frequency is given and the channel bandwidth is known, the upper and lower frequency limits of the channel can be easily derived. For example, a channel with a 2 kHz (2,000 Hz) bandwidth centered at 100 kHz occupies the spectrum between 99 kHz and 101 kHz.
The UHF and SHF bands have further subdivisions, with bands that are used for terrestrial radio links, satellite links, and for satellite broadcasting. These include the L, Cyan, X, Ku, IC, and Ka bands, with frequencies ranging from about 1 GHz to 40 GHz.
United States Frequency Allocations Chart
The United States Department of Commerce, National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) - Office of Spectrum Management released this chart to the public in 2003. This is an enormous chart that would make an excellent poster to hang on your wall. It is very detailed. Click the icon below for a direct link to the file.
The NTIA's Office of Spectrum Management is in charge of regulating use of spectrum allocated to the Federal Government. It serves in a manner equivalent to the FCC for this purpose. It is also the part of the Department of Commerce that oversees ICANN.
Wavelength Table
Meter Band Frequency Range and Use -------------------------------------------------- 160 meter 1800 - 2000 kHz ham radio 120 meter 2300 - 2498 kHz broadcasting 90 meter 3200 - 3400 kHz broadcasting 80 meter 3500 - 4000 kHz ham radio 60 meter 4750 - 4995 kHz broadcasting 49 meter 5950 - 6250 kHz broadcasting 41 meter 7100 - 7300 kHz broadcasting 40 meter 7000 - 7300 kHz ham radio 31 meter 9500 - 9900 kHz broadcasting 30 meter 10100 - 10150 kHz ham radio 25 meter 11650 - 11975 kHz broadcasting 22 meter 13600 - 13800 kHz broadcasting 20 meter 14000 - 14350 kHz ham radio 19 meter 15100 - 15600 kHz broadcasting 17 meter 18068 - 18168 kHz ham radio 16 meter 17550 - 17900 kHz broadcasting 15 meter 21000 - 21450 kHz ham radio 13 meter 21450 - 21850 kHz broadcasting 12 meter 24890 - 24990 ham radio 11 meter 25670 - 26100 kHz broadcasting 10 meter 28 - 29.7 MHz ham radio 6 meter 50 - 54 MHz ham radio since 1947 5 meter 56 – 64 MHz taken from ham radio in 1946 4 meter 70.000 MHz – 70.500 MHz 3 meter 76 - 88 MHz 88 - 108 MHz broadcasting 2 meter 144 MHz to 148 MHz for ham 1.25 meter 219 - 225 MHz 70 centimeter 420 - 450 MHz ham 462 - 468 MHz non-ham public 33 centimeter 902.000 MHz – 928.000 MHz 23 centimeter 1.240 GHz – 1.300 GHz 13 centimeter 2.300 GHz – 2.450 GHz
Due to errors from HAM designations versus actual wave conversion formula 17-meter ham radio band is actually higher in frequency than the 16-meter broadcasting band.
| Band name | Abbreviation | ITU band | Frequency and wavelength in air |
Example uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tremendously low frequency | TLF | < 3 Hz > 100,000 km |
Natural and artificial electromagnetic noise | |
| Extremely low frequency | ELF | 3–30 Hz 100,000 km – 10,000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Super low frequency | SLF | 30–300 Hz 10,000 km – 1000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Ultra low frequency | ULF | 300–3000 Hz 1000 km – 100 km |
Submarine communication, communication within mines | |
| Very low frequency | VLF | 4 | 3–30 kHz 100 km – 10 km |
Navigation, time signals, submarine communication, wireless heart rate monitors, geophysics |
| Low frequency | LF | 5 | 30–300 kHz 10 km – 1 km |
Navigation, clock time signals, AM longwave broadcasting (Europe and parts of Asia), RFID, amateur radio |
| Medium frequency | MF | 6 | 300–3000 kHz 1 km – 100 m |
AM radio (medium-wave) broadcasts, amateur radio, avalanche beacons |
| High frequency | HF | 7 | 3–30 MHz 100 m – 10 m |
Shortwave broadcasts, citizens' band radio, amateur radio and over-the-horizon aviation communications, RFID, over-the-horizon radar, automatic link establishment (ALE) / near-vertical incidence skywave (NVIS) radio communications, marine and mobile radio telephony |
| Very high frequency | VHF | 8 | 30–300 MHz 10 m – 1 m |
FM radio, television broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to-aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications, land mobile and maritime mobile communications, amateur radio, weather radio |
| Ultra high frequency | UHF | 9 | 300–3000 MHz 1 m – 100 mm |
Television broadcasts, microwave oven, microwave devices/communications, radio astronomy, mobile phones, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee, GPS and two-way radios such as land mobile, FRS and GMRS radios, amateur radio |
| Super high frequency | SHF | 10 | 3–30 GHz 100 mm – 10 mm |
Radio astronomy, microwave devices/communications, wireless LAN, most modern radars, communications satellites, satellite television broadcasting, DBS, amateur radio |
| Extremely high frequency | EHF | 11 | 30–300 GHz 10 mm – 1 mm |
Radio astronomy, high-frequency microwave radio relay, microwave remote sensing, amateur radio, directed-energy weapon, millimeter wave scanner |
| Terahertz or Tremendously high frequency | THz or THF | 12 | 300–3,000 GHz 1 mm – 100 um |
Terahertz imaging – a potential replacement for X-rays in some medical applications, ultrafast molecular dynamics, condensed-matter physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, terahertz computing/communications, sub-mm remote sensing, amateur radio |
frequency band meter