Difference between revisions of "A/C Electrical Wiring Information for North America"
m (→Earth Ground) |
m (→Install Residential Grounding Rod) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=== Install Residential Grounding Rod === | === Install Residential Grounding Rod === | ||
| − | Grounding rods are driven into the earth to a depth of at least 8 feet. If rock is hit at less than 8 feet, the grounding rod can be driven at an angle but the angle cannot exceed 45 degrees. A grounding rod can also be buried on top of rock in a trench that is 2 1/2 feet deep and 8 feet long. Ground clamps hold the ground conductor and the grounding rod together without losing conductivity when exposed to weather and movement. | + | [[Image:6awgwriteforearthground.png]] |
| + | |||
| + | Grounding rods are driven into the earth to a depth of at least 8 feet. If rock is hit at less than 8 feet, the grounding rod can be driven at an angle but the angle cannot exceed 45 degrees. A grounding rod can also be buried on top of rock in a trench that is 2 1/2 feet deep and 8 feet long. Ground clamps hold the ground conductor and the grounding rod together without losing conductivity when exposed to weather and movement. When the resistance of a single ground rod exceeds 25 ohms, an additional ground rod installed not less than 6 feet away is required. | ||
| | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 10 July 2008
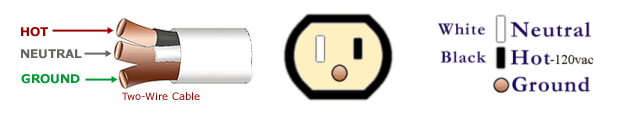
Wire Color Standard
- White - Neutral ..... (grounded conductor, neutral conductor, neutral point) conductor with continuity to the electrical system's center tap of the power company transformer.
- Black - Hot 110v / 120v ..... (positive, power) not grounded, the active wire which is most likely to electrocute a person. This is the dangerous wire!
- Bare - Ground ..... (grounding wire, earth ground) a conductor with continuity to earth, may be bare or identified insulated wire of green or having green stripes.
- Red - Hot 110v / 120v
Standard Wire
Earth Ground
A true earth ground, as defined by the National Electrical Code, physically consists of a conductive pipe or rod driven into the earth to a minimum depth of 8 feet.
A house ground is easy to find, all you have to do is look outside at the power feed coming in, there should be a thick bare wire coming down the side of the structure that attaches to either a steel pipe or a thick rod, driven into the ground. The neutral is tied to earth ground for lightning protection and to provide a path for any high voltage leakage from the power company's step down transformer. The ground is tied to the neutral to provide a return path to trip the breaker in the event of a fault. The main breaker box should be the only point where neutral/ground need to be connected, never at the outlets or other places in the electrical system.
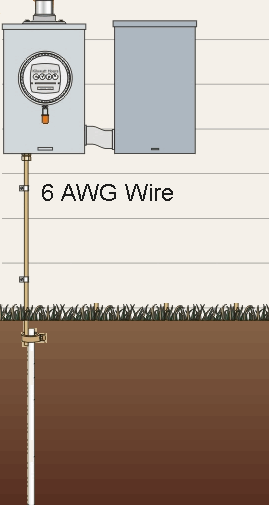
Install Residential Grounding Rod
Grounding rods are driven into the earth to a depth of at least 8 feet. If rock is hit at less than 8 feet, the grounding rod can be driven at an angle but the angle cannot exceed 45 degrees. A grounding rod can also be buried on top of rock in a trench that is 2 1/2 feet deep and 8 feet long. Ground clamps hold the ground conductor and the grounding rod together without losing conductivity when exposed to weather and movement. When the resistance of a single ground rod exceeds 25 ohms, an additional ground rod installed not less than 6 feet away is required.