Difference between revisions of "Bows and Arrows Basic Reference"
From Free Knowledge Base- The DUCK Project: information for everyone
m |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Long Bow == | == Long Bow == | ||
| − | == Compound Bow | + | == Compound Bow == |
| + | [[Image:CompoundBow01.gif]] | ||
[[Category:Sports and Recreation]] | [[Category:Sports and Recreation]] | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 29 June 2007
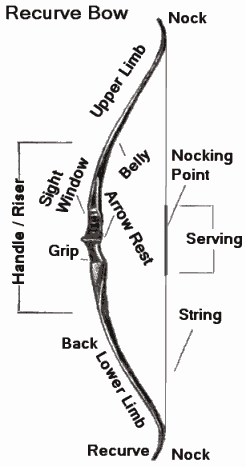
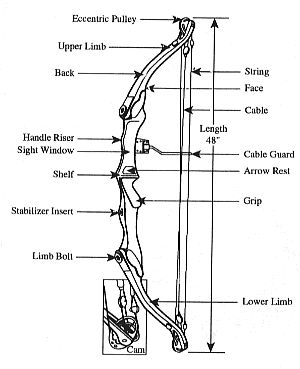
Archery is usually done using recurve bow, longbow, or compound bow. Of these, the recurve is overwhelmingly the most popular. All bows have largely the same essential components.
- Limbs which bend when the string is drawn, and store the energy used to propel the arrow. Bow limbs are generally constructed of man-made materials, such as fiberglass, carbon and syntactic foam. The limbs store the energy of the draw and release it to the arrow.
- A riser which is the handle part between the limbs. In a one piece bow, the riser and the limbs are, of course, the same piece of material. The riser will usually be made of wood or metal.
- The string is usually made of either "Fast Flight", a hydrocarbon product that also has medical and other uses, or "Kevlar", the material used to make bullet-proof vests. The reinforced bit in the middle is called the serving. Towards the middle of the serving is the nocking point, where the arrow is mounted.
- An arrow shelf or arrow rest on the riser. This supports the arrow while it is drawn. A shelf is a cutting into the bow riser itself, while a rest is something mounted on the side of the riser. An extended shelf cutout is sometimes referred to as a sight window. Some bows have both shelf and riser; traditional longbows have neither.