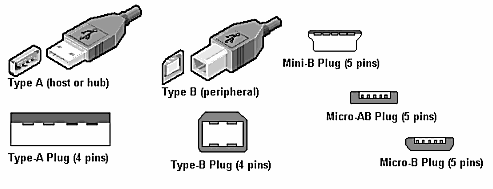
USB Connector Types
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a standard developed that defines the cables, connectors and communication protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power between computers and electronic devices.
The connector designs were specified by the USB committee. The connector mounted on the host or device is called the receptacle, and the connector attached to the cable is called the plug. The terms male and female represent the plug, and receptacle respectively.
There's a variety of USB cables, including micro-USB, mini-USB, and standard USB.
Contents
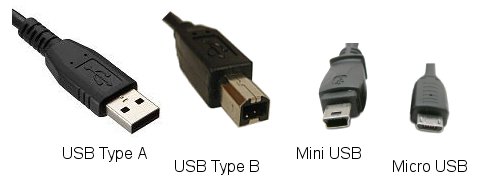
USB Type A
The USB A connector is used on devices which provide power (mostly computers). These devices are known as the host. The host, typically a computer, will supply power as well as optional data transfer capabilities (the computer always will.)
These come in the Standard A plug and Standard A receptacle.
USB Type B
Standard-B plug or USB B connector is used on devices which receive power like most peripherals such as modern printers or bed scanners. These devices are known as peripherals and have only slave functionality. They charge or are powered by the voltage they receive from a host device, along with having optional data transfer capabilities.
USB Mini
Mini USB connectors are smaller than their standard USB counterparts and feature a fifth pin. The fifth pin is known as the ID pin and is typically of no use in mini USB connectors.
Mini-A plug
This connector type is rare and has been officially withdrawn from the standard. Type 'A' devices are considered to supply power. Small devices are not used to supply power, they tend to require power, such as a cell phone requires power to charge. Those that require power then fall into the type 'B' category.
Mini-B plug
For devices where the Standard-B connector would be too large. Some cell phones, such as the Motorola RAZR V3, or smaller devices, such as the Neat Receipts portable sheet scanner, and even gaming devices, such as Sony Play Station 3 controllers, all use the USB Mini B Standard.
USB Micro
A need for yet a thinner, smaller connector type was perceived and USB Micro was introduced to surpass the mini USB standard. Although the micro USB connector is much thinner than the mini, it has been especially designed for rough use and the connector will hold up under more connects and disconnects.
Standard devices will use Micro-B receptacles, while USB OTG (On-The-Go) devices will use Micro-AB receptacles.
Micro-AB plug
In the portable device world it became necessary to accommodate a new circumstance where a portable device may act as a host device as well as a slave device. A mobile device such as a tablet or smart phone may be connected directly to a printer. This makes the mobile device, which has historically been a slave device, assume the role of a host device, supplying power to the peripheral such as a printer.
USB On-The-Go is an extension to the USB specification allowing a micro USB to serve as A or B type, thus USB On-The-Go is Micro-AB. This supplement provides means for easy switching between the master and slave role of a device. There is a push in some countries to mandate that Micro-AB become the standard for all mobile devices such as smartphones.
Micro-AB receptacles will accept both Micro-A and Micro-B plugs.
Micro-B plug
The Micro USB standard has gained popularity and is predominate on all modern mobile devices. Almost all cell phones use this connector type for the charger and data transfer connection.
Micro-B receptacles will accept only Micro-B plugs.
USB-C
The USB Type-C replaces USB Micro (MicroUSB) which was the most popular connector for non-Apple mobile devices and accessories made between 2008 and 2016. Now these devices will be uses the new ovaloid connector which unlike MicroUSB, can be connected either way (there is no upside down). Android and Windows mobile devices made after 2015 will use USB-C which gives us yet another connector type to further confuse consumers. Since USB-C is a very small connector, some individuals may not note the subtle difference in shape and attempt using MicroUSB a charger which will not insert into the device.
USB 3.1 Type-C cables offer a transfer rate of 10Gbps, which is double the transfer speed of USB 3.0 (5 Gbps). Additionally, these cables will offer 20 volts and 5 amps of power, compared with the 5 volts and 1.8 amps of its predecessor.
Other proprietary connectors
30-pin Apple
The old very wide and thin connector from the iPod and other Apple devices used between 2003 and 2012.
Lightning
Apple has always marched to the beat of a different drum despite creating more consumer confusion. Their lightning connector has prominent gold lines on either side of its slim plug, and it can be inserted either way up.
illustrations
Common USB Connectors
Compare New Connectors
Related Information
Motorola Cell Phone Unauthorized Charger
You connect your Motorola Razor to a phone charger with the miniUSB connector. Instead of charging, you get the Motorola Cell Phone Unauthorized Charger Message.
New USB 3.0 Interface
The USB 3.0 Interface has backward compatibility with USB 2.0; you need a new cable and new host adapter. The USB 3.0 connector has a front row of four pins for the USB 1.x/2.0 backwards compatibility, and a second row of five pins for the new USB 3.0 connectivity.
Related
- Micro USB Charger Compatibility
- USB Connector Types
- USB 3.0 Interface
- Sony Playstation 3