Bows and Arrows Basic Reference
From Free Knowledge Base- The DUCK Project: information for everyone
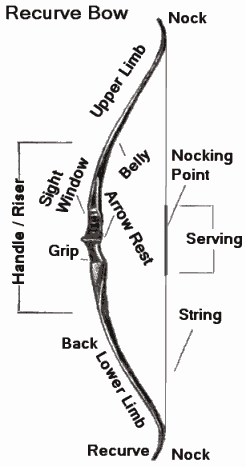
Archery is usually done using recurve bow, longbow, or compound bow. Of these, the recurve is overwhelmingly the most popular. All bows have largely the same essential components.
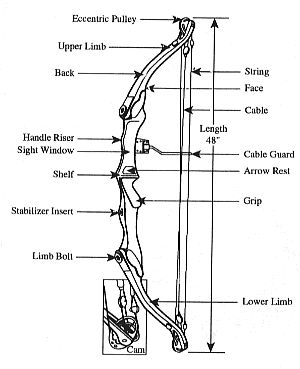
- Limbs which bend when the string is drawn, and store the energy used to propel the arrow. Bow limbs are generally constructed of man-made materials, such as fiberglass, carbon and syntactic foam. The limbs store the energy of the draw and release it to the arrow.
- A riser which is the handle part between the limbs. In a one piece bow, the riser and the limbs are, of course, the same piece of material. The riser will usually be made of wood or metal.
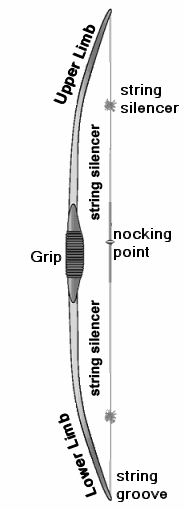
- The string is usually made of either "Fast Flight", a hydrocarbon product that also has medical and other uses, or "Kevlar", the material used to make bullet-proof vests. The reinforced bit in the middle is called the serving. Towards the middle of the serving is the nocking point, where the arrow is mounted.
- An arrow shelf or arrow rest on the riser. This supports the arrow while it is drawn. A shelf is a cutting into the bow riser itself, while a rest is something mounted on the side of the riser. An extended shelf cutout is sometimes referred to as a sight window. Some bows have both shelf and riser; traditional longbows have neither.
Recurve Bow
|
Most recurve bows are five to six feet in length. Some are designed to come apart into pieces for travel and storage, they are referred to as a “takedown” bow. To ensure potential energy is stored evenly within the limbs during the draw, the modern recurve bow tips point to the target when unstrung, and parallel to the bowstring when strung. The bow handle (riser) will have a cut out on one side where the arrow rests. This is one way to distinguish a modern recurve bow from a longbow. The longbow has no such rest for the arrow. |