Difference between revisions of "Machine Screw"
From Free Knowledge Base- The DUCK Project: information for everyone
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. A machine screw is typically designed to be fastened to an existing, tapped hole on a metal surface. | The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. A machine screw is typically designed to be fastened to an existing, tapped hole on a metal surface. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 29: | ||
Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi) | Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi) | ||
| − | + | {{:Sparce Entry}} | |
| | ||
Revision as of 21:07, 6 February 2014
The machine screw is an element of construction, a type of threaded fastener. A machine screw is typically designed to be fastened to an existing, tapped hole on a metal surface.
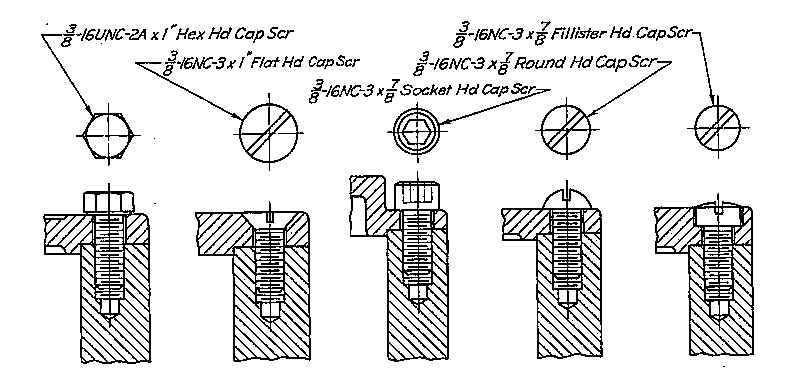
Example: Standard Cap Screws
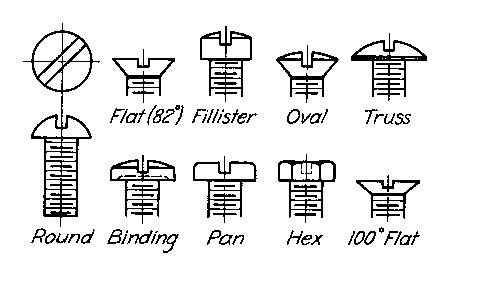
Example: Standard Machine Screw Head Types
Screw bit types:
- Slotted
- Phillips
- Combination
- Torx
- Star
- Hex (internal)
- Hex (external)
- JIS
- Phillips Square
- Square
the standard Computer Case Screw size is 6-32.
Unified Thread Standard (UTS)
The following formula is used to calculate the major diameter of a numbered screw greater than or equal to 0: Major diameter = Screw # × 0.013" + 0.060". For example, a number 10 calculates as: #10 × 0.013" + 0.060" = 0.190" major diameter.
Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi)
- redirect Template:Sparse Entry